
Heath Insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance is risk among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement.[1] The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity. According to the Health Insurance Association of America, health insurance is defined as "coverage that provides for the payments of benefits as a result of sickness or injury. It includes insurance for losses from accident, medical expense, disability, or accidental death and dismemberment.
There are two basic types of health insurance
1. Mediclaim Plans
Mediclaim or hospitalisation plans are the most basic type of health insurance plans. They cover the cost of treatment when you are admitted to the hospital. The payout is made on actual expenses incurred in the hospital by submitting original bills. Most of these plans cover the entire family up to a certain limit.
2. Critical Illness Insurance Plans
Critical Illness Insurance Plans cover specific life-threatening diseases. These diseases could require prolonged treatment or even change in lifestyle. Unlike hospitalisation plans, the payout is made on Critical Illness cover chosen by the customer and not on actual expenses incurred in the hospital. The cover gives the flexibility to use the monies for changing lifestyle and medicines. Also it's a substitute for income for the time you could not resume work due to illness. Payout under these plans are made on the diagnosis of the disease for which the original medical bills are not required.
Health Insurance In India[edit]
Main article: Healthcare in India
In India, provision of health care services varies state-wise. Public health services are prominent in most of the states,
but due to inadequate resources and management, major population opts for private health services.
To improve the awareness and better health care facilities, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India and The General Corporation of India runs health care campaigns for the whole population. IN 2018, for under privileged citizens, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the launch of a new public health insurance fund called Ayushman Bharat Yojana and the government claims that the new system will try to reach more than 500 million people.
In India, Health insurance is offered mainly in two Types:
• Indemnity Plan
basically covers the hospitalisation expenses and has subtypes like Individual Insurance, Family Floater Insurance, Senior Citizen Insurance, Maternity Insurance, Group Medical Insurance.
• Fixed Benefit Plan
pays a fixed amount for pre-decided diseases like critical illness, cancer, heart disease, etc. It has also its sub types like Preventive Insurance, Critical illness, Personal Accident.
Depending on the type of insurance and the company providing health insurance, coverage includes pre-and post-hospitalisation charges, ambulance charges, day care charges, Health Checkups, etc.
It is pivotal to know about the exclusions which are not covered under insurance schemes:
- Treatment related to dental disease or surgeries
- All kind of STD's and AIDS
- Non-Allopathic Treatment
Few of the companies do provide insurance against such diseases or conditions, but that depends on the type and the insured amount. Some important aspects to be considered before choosing the health insurance in India are Claim Settlement ratio, Insurance limits and Caps, Coverage and network hospitals.
Some Of The Key Players In Health Insurance Sector in India
Below is the list of top health insurance companies in India along with their claim settlement ratio as per FY 2019-2020.
| Rank | Health Insurance Company | Health Claim Settlement Ratio | Network Hospitals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IFFCO Tokio General Insurance | 96.33% | 1416 |
| 2 | Care Health Insurance | 95.47% | 2500 |
| 3 | Magma HDI Health Insurance | 95.17% | 5016 |
| 4 | The Oriental Insurance Company | 93.96% | NA |
| 5 | New India General Insurance | 92.68% | 1256 |
| 6 | Bajaj Allianz General Insurance | 92.24% | 6277 |
| 7 | Max Bupa Health Insurance | 89.46% | 5270 |
https://www.insurancedekho.com/health-insurance/companies#popup
Current Health Insurance Market In India :
The health insurance industry in India is the fastest growing segment in the non-life insurance sector. The market witnessed a robust double digit growth of 24% in FY 17, with a market share of 24%, in the entire non-life insurance sector. It has been the fastest growing market segment, registering a CAGR of 23%, for the past 10 years. This phenomenal growth may be attributed to the liberalization of the economy and growing general awareness among the public on healthcare.
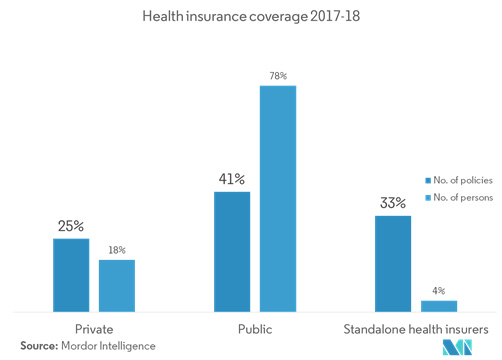
The health insurance industry is at an embryonic stage, with roughly 25% of the population under its coverage. There exists a huge potential for growth and penetration of health insurance to a larger population. Additionally, there are both opportunities and restraints in the marketing and distribution of health insurance products in India. This report is an attempt to uncover the prospects of successful marketing of such products from the standpoint of insurance marketers, and look at issues impeding the growth of the health insurance market in India.
The launch of National Health Protection Scheme under Ayushman Bharat, in September 2018, in order to provide coverage of up to INR 500,000 (USD 7,723) to more than 100 million vulnerable families, holds heavy expectations, which increases penetration of health insurance in India, from nearly 34% to 50%. Also, about 47.9 million farmers benefitted under Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) in 2017-2018.
Health insurance sector market size India FY 2018-2030 Published by Statista Research Department, Mar 25, 2021
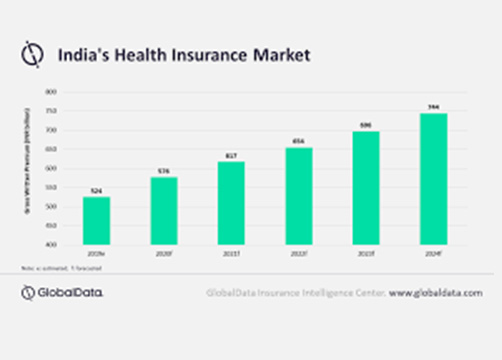
https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/india-health-and-medical-insurance-market https://www.statista.com/statistics/1116457/india-health-insurance-sector-market-size/
The market size of the Indian health insurance sector was about 370 billion Indian rupees in financial year 2018. This was projected to cross over two trillion rupees by financial year 2030. This growth was projected taking into account the rising income levels, increasing awareness in urban areas and growing lifestyle related health demands. Market size of the health insurance sector was calculated by taking into account the number of lives covered and the price per life.
Opportunities.
The possibility of future growth of this sector is high, as penetration in the rural sector is low. The improvement of technology and the use of internet facility are helping this sector to grow in magnitude and move towards environment-friendly paperless regime
https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/XJM-07-2020-0021/full/html
Conclusion:
Health insurance is like a knife. In the surgeon’s hand it can save the patient, while in the hands of the quack, it can kill. Health insurance is going to develop rapidly in future. The main challenge is to see that it benefits the poor and the weak in terms of better coverage and health services at lower costs without negative aspects of cost increase and overuse of procedures and technology in provision of health care.
http://www.actuariesindia.org/downloads/gcadata/10thGCA/Emerging%20Health%20Insurance%20in%20India-An%20
Garima Bharati- Sr. HR Consultant
- Healthcare Ecommerce/Retail
Mayukhi Saha- HR Consultant
- Hospital & Healthcare Delivery
Sujoy Ghosh
- Pharma & Diagnostic
Ripshika Dey- HR Consultant
- Medical Device
Samarpita Misra- HR Consultant
- Clinical Research Organization & R&D services
Poulami S. Neogi- HR Consultant
- Health Insurance/TPA
Dipalok Biswas- HR Consultant
- Healthcare IT

